Debt Mutual Funds are a stable investment option that primarily invests in fixed-income securities. This post covers all types of debt-oriented mutual funds that you should know to make an informed financial decision.
Understanding Debt Mutual Funds
Debt mutual funds primarily invest in fixed-income securities like government bonds, corporate bonds, treasury bills, and money market instruments. They aim to provide steady returns with lower risk compared to equity funds.
These funds do not invest in equity stocks. To know all the types of equity mutual funds, check out this post on Equity Mutual Funds.
4 Reasons Why Anyone Will Invest In Debt Mutual Funds?
Reason 1: IF you don’t want to invest in the stock market due to volatility. Most of these funds offer interest rates better than those from fixed deposits. They are less risky and provide consistent returns.
Reason 2: You should diversify your investments across different asset classes. You want high returns from equity instruments and also want consistent returns with less volatility on the other side. Then not only in Equity mutual funds, you should also allocate a certain portion of funds to debt mutual funds. With the help of STP(Systematic Transfer Plan), you can transfer your funds from debt to Equity funds or vice versa each month based on market conditions.
Reason 3: SEBI’s categorisation of debt mutual funds offers a variety of options tailored to different financial goals, risk appetites, and investment horizons. From ultra-safe overnight funds to long-duration funds and dynamic bond funds, there’s a debt fund for every type of investor. So why don’t you think about investing in debt funds?
Reason 4: Many debt funds, such as liquid and ultra-short-duration funds, offer high liquidity, allowing you to withdraw your money quickly when needed. This makes them a suitable option for short-term goals, parking surplus cash, or maintaining an emergency fund.
To know more about emergency funds and the best way to maintain them check this out Emergency Fund
Here is the SEBI’s circular released in 2017 covering mutual fund schemes SEBI Circular
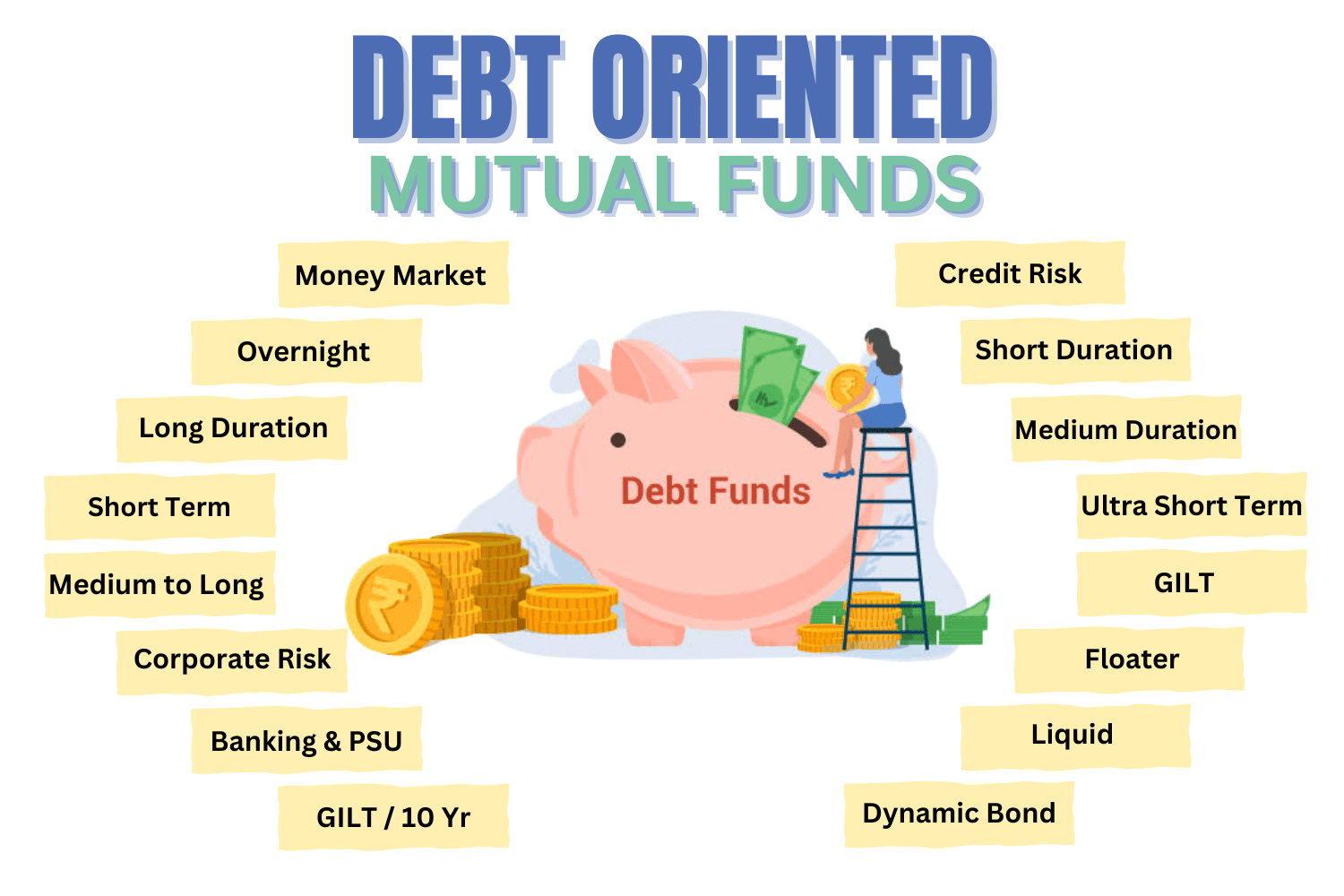
Let’s have a look at the different types of debt-oriented mutual funds:
1. Very Short Duration Funds
- Overnight Fund: Invests in overnight securities with a maturity of one day. These funds are ideal for investors seeking a safe place to park surplus funds for a very short period.
- Liquid Fund: Invests generally in debt and money market securities with a maturity of up to 91 days. Suitable for investors looking for high liquidity and minimal risk, often used as an alternative to savings accounts.
- Ultra Short Duration Fund: Invests in debt and money market instruments with a Macaulay duration between 3 to 6 months. These funds offer slightly higher returns than liquid funds with a marginal increase in risk.
2. Short Duration Funds`
- Low Duration Fund: Invests in debt and money market instruments with a Macaulay duration between 6 to 12 months. Suitable for investors with an investment horizon of around a year, offering a balance between risk and return.
- Money Market Fund: Invests in money market instruments with an investment horizon of up to one year. These funds aim to provide high liquidity with low risk, making them suitable for short-term investment goals.
- Short Duration Fund: Invests in debt and money market instruments with a Macaulay duration between 1 to 3 years. Ideal for investors with a short to medium-term investment horizon seeking stable returns.
3. Medium-Term Debt Funds
- Medium Duration Fund: Invests in debt and money market instruments with a Macaulay duration between 3 to 4 years. Suitable for investors with a medium-term investment horizon looking for moderate returns.
- Banking & PSU Fund: Invests a minimum of 80% in debt instruments of banks, public sector undertakings, public financial institutions, and municipal bonds. These funds are considered relatively safer due to the high credit quality of the issuers.
- Corporate Bond Fund: Invests a minimum of 80% in corporate bonds rated AA+ and above. Ideal for investors seeking higher returns with moderate risk exposure.
4. Long-Term Debt Funds
- Medium to Long Duration Fund: Invests in debt and money market instruments with a Macaulay duration between 4 to 7 years. Suitable for investors with a longer investment horizon willing to take on higher interest rate risk for potential returns.
- Long Duration Fund: Invests in debt and money market instruments with a weighted average time to maturity greater than 7 years. These funds are sensitive to interest rate changes and are suitable for investors with a high-risk appetite and long-term investment goals.
- Dynamic Bond Fund: Invests across durations, actively managing the portfolio based on interest rate movements. Suitable for investors seeking flexibility and professional management of interest rate risk.
5. Government Securities (Gilt) Funds
- Gilt Fund: Invests a minimum of 80% in government securities across maturities. These funds carry minimal credit risk as they are backed by the government but are subject to interest rate risk.
- Gilt Fund with 10-year Constant Duration: Invests a minimum of 80% in government securities such that the Macaulay duration of the portfolio is equal to 10 years. Suitable for investors looking to invest in long-term government securities with a specific duration.
6. Other Debt Funds
- Target Maturity Funds: These funds have a defined maturity date and invest in bonds that mature close to the fund’s maturity. They are suitable for investors looking to align their investment horizon with the fund’s maturity.
- Floater Fund: Invests a minimum of 65% in floating rate(rate keeps on changing) instruments, which have interest rates that reset periodically. These funds benefit from rising interest rates and are suitable for investors looking to mitigate interest rate risk.
- Credit Risk Fund: Invests a minimum of 65% in corporate bonds rated AA and below. These funds aim to generate higher returns by taking on higher credit risk and are suitable for investors with a higher risk tolerance.
- Retirement Solution-Oriented Funds: As the name suggests, designed specifically for retirement planning these funds have a lock-in period and invest in a mix of equity and debt instruments to provide growth and stability.
- Index Funds: These funds replicate a specific bond index, providing investors with exposure to a diversified portfolio of bonds that match the index’s composition.
Major Risks Involved in Debt Mutual Funds.
Credit Risk: There is no guarantee that your money invested into the fund will get back to you. Mutual funds always advertise “Read all the related documents carefully and returns are subject to market risks” tagline everywhere. Funds might not get money back from the place where they invested. Consider the experienced and reputed debt funds to avoid credit risk.
Interest Rate Risk: The value of debt funds depends on the movement of interest rates in the economy. These funds invest in bonds and bonds and interest rates have an inverse relationship. If bond prices go up, the interest rate comes down, and vice versa. Dynamic and long duration funds are more effected by interest rate movements. Short-term investors should stick to funds with lower durations to minimise interest rate risk. This is the big risk involved in all types of debt-oriented mutual funds.
Conclusion:
Debt mutual funds serve as an excellent tool to diversify portfolios and achieve balanced growth. Whether you’re a conservative investor prioritizing safety or someone seeking slightly higher yields with managed risk, there’s debt-oriented funds are the ones you can consider after thorough research.






I had the pleasure of reading this post on Debt Oriented Mutual Funds and I must say it’s exceptionally well-written and insightful. This content on different types gives me a diversified yet detailed analysis on risk, returns, and the suitability of these funds. Keep up the excellent work—your content is a true asset to the financial education space!
Thank you Bhavitha 🙂, your feedback is valuable. Do subscribe to our weekly newsletter.